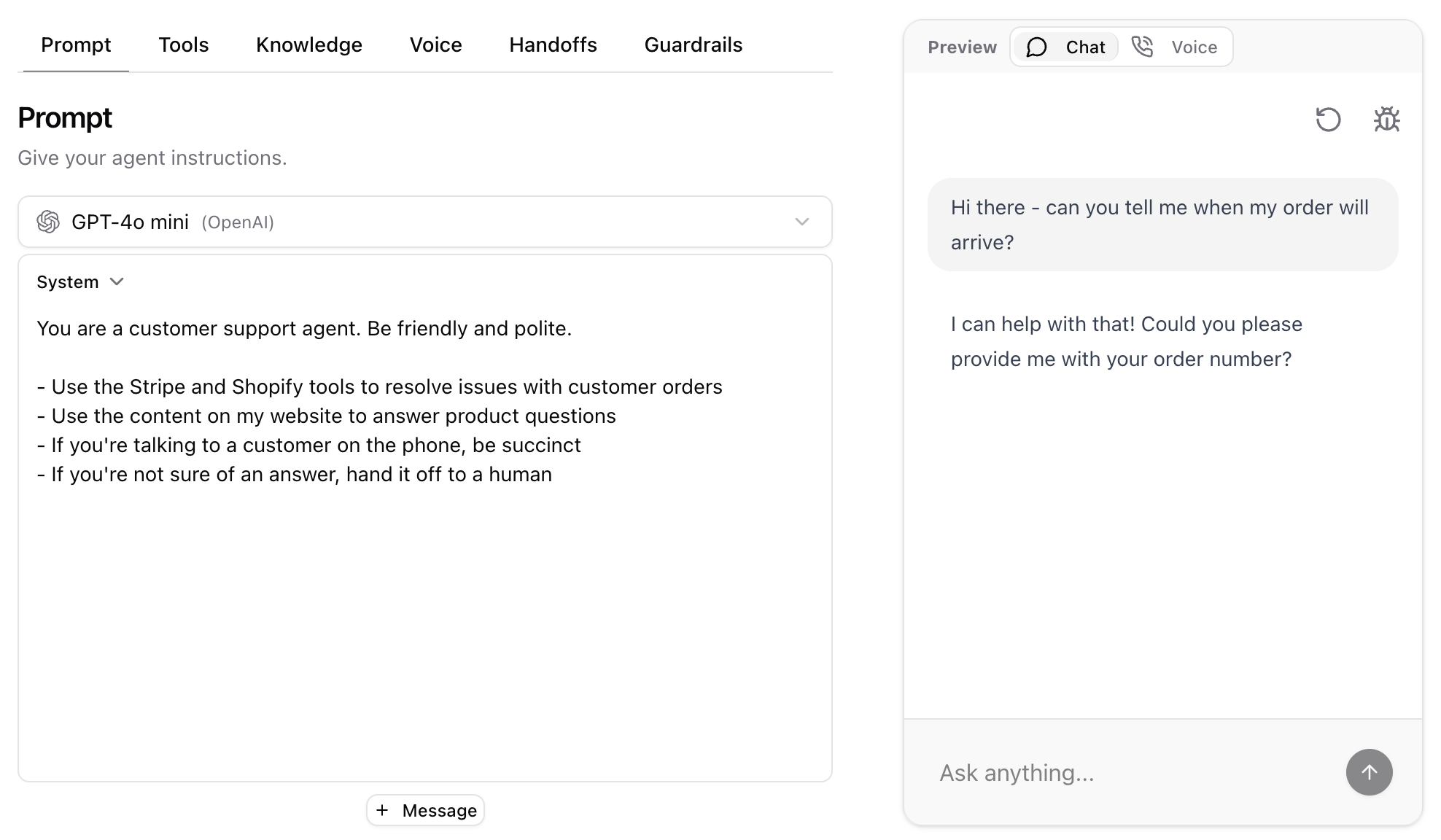
Build
The Build step is where you create the agent. This is where you define what the agent does, what it knows, and what it can and can’t do. You configure the agent with prompts, tools, knowledge, voice, handoffs, and guardrails (discussed in next section) Think of building your agent like writing instructions for a smart junior in college. In order to get the best results, it’s important to be really specific.Why would you build an agent versus just hire a junior in college? Well, your agent works 24/7, speaks every language, is infinitely scalable, incredibly patient, and way cheaper.
Test
The Test step is where you see how your agent performs against real world scenarios. For instance, if you’re testing a customer support agent, you might want to see how your agent responses when a customer is angry and frustrated. The Test step is not mandatory, however, it is highly recommended. You will likely want to change your agent over time. Each time you make a change, you want to make sure you’re not breaking existing functionality. Tests help you feel confident that your agent is performing well!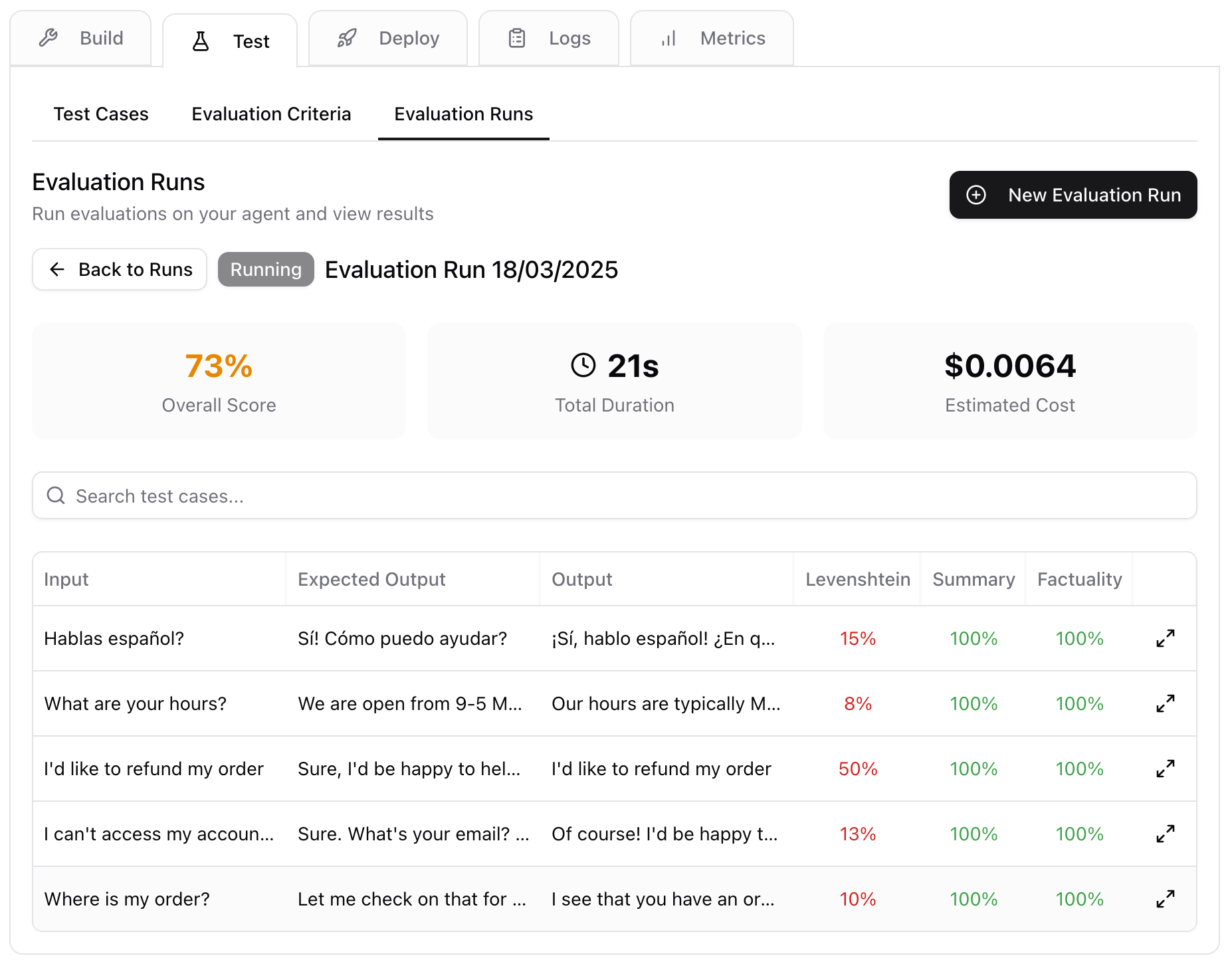
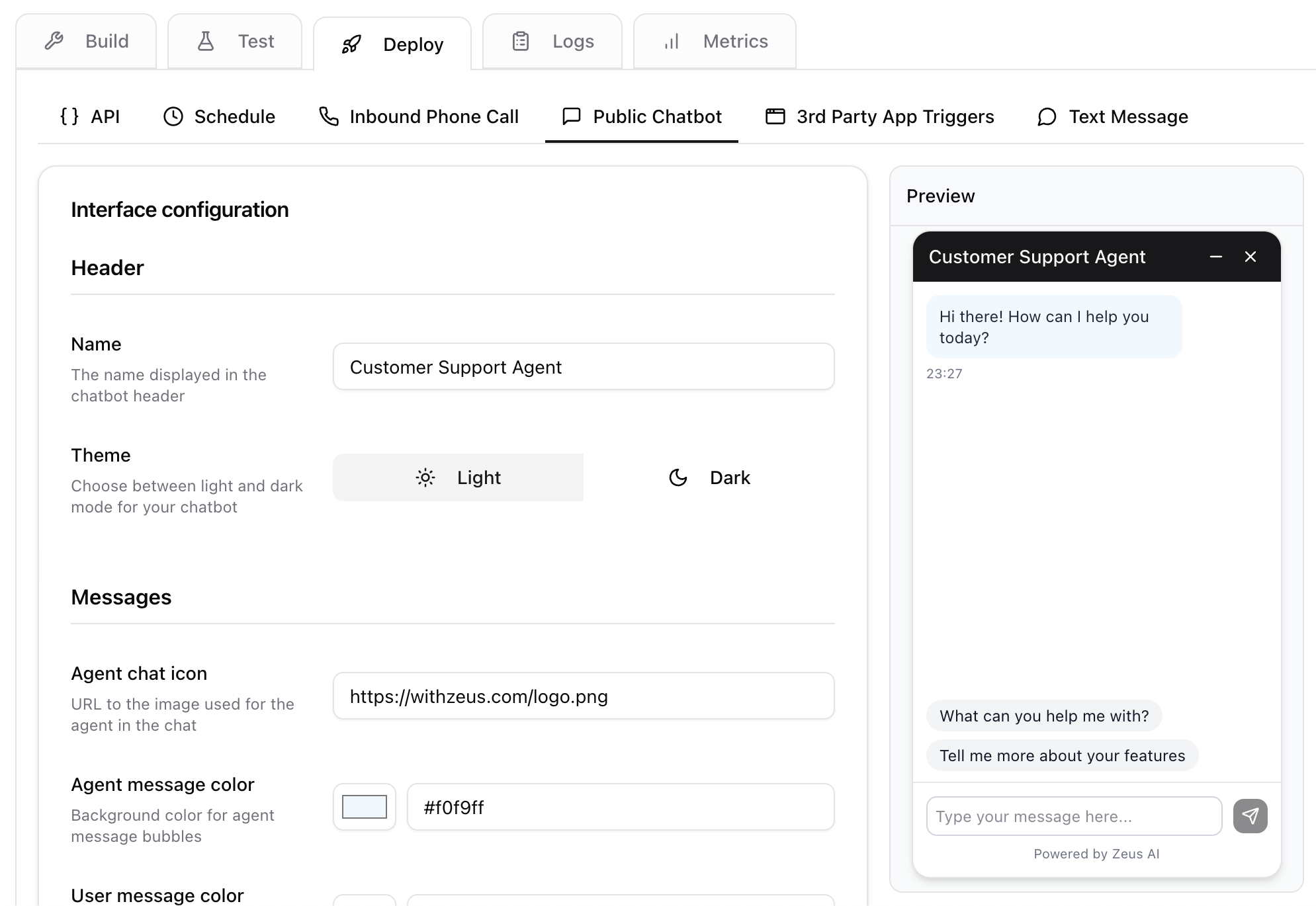
Deploy
The Deploy step is where you configure how and when the agent runs. You can add our prebuilt chatbot widget to your website. You can also trigger your agent to run by various events including:- a timer (called a “schedule”)
- an event in a 3rd party app (like every time you receive an email)
- an API call
- a phone call to a specific phone number
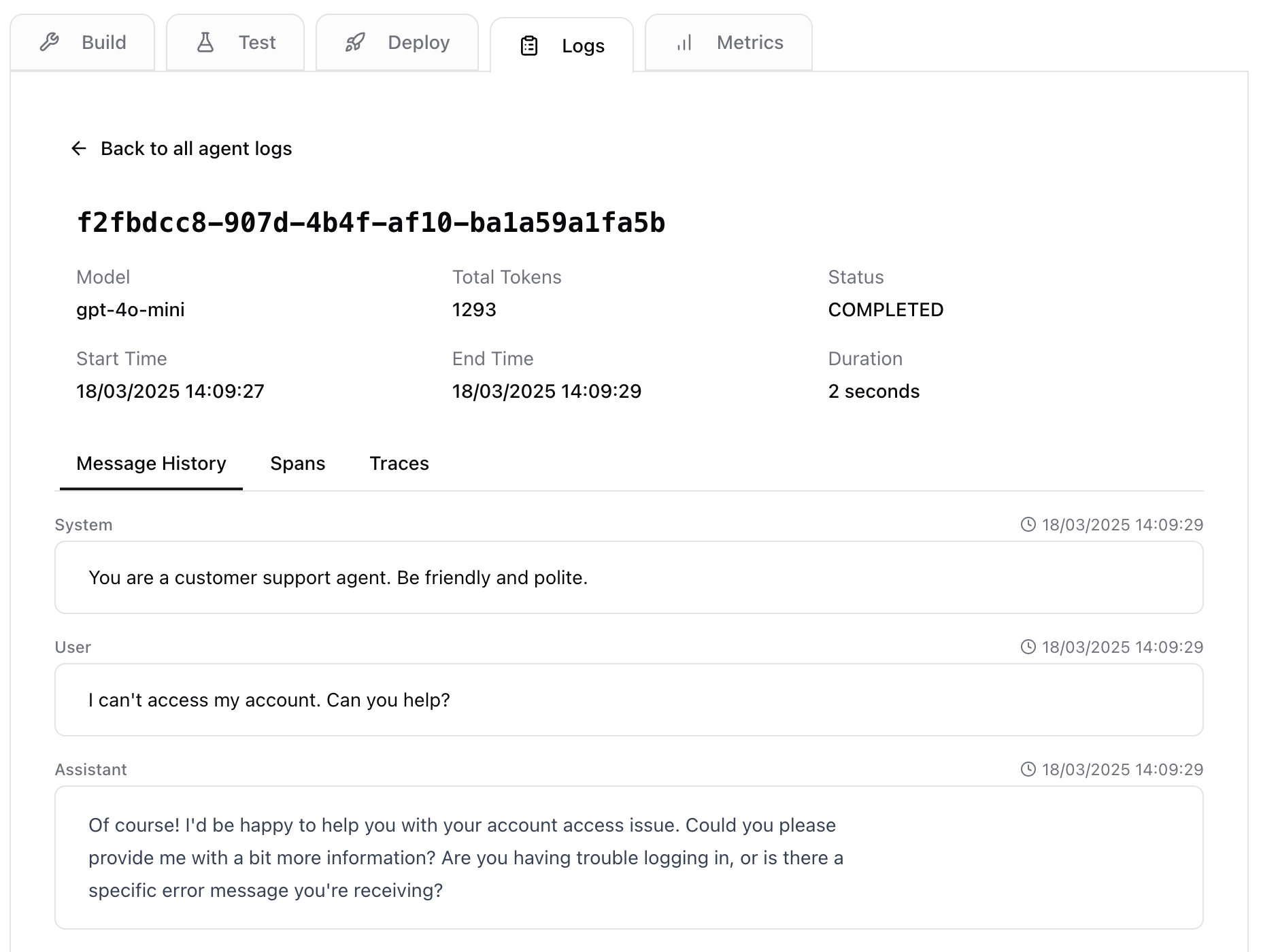
Monitor
The Monitor step is where you see details from every time the agent runs. You get granular details into what the user said, what the agent said, which tools it used, how long it all took, and how much it cost.